Can you get an STD from Handjobs?
Sexually Transmitted Diseases (STDs) remain a serious threat in today’s sexual exploration and intimacy environments. Despite increasing discussions regarding safe sex practices and STD prevention. Although misconceptions may remain regarding whether handjobs can transmit STDs. We explore both facts and myths regarding this topic in this article.
Understanding STDs and How They Spread
Before addressing a specific question about STDs, we must understand their transmission. Sexually transmitted diseases (STDs) are infections caused by bacteria, viruses, or parasites and transmitted through intimate sexual contact such as vaginal, anal, and oral sex. Some forms may also spread via blood donation or sharing contaminated needles. This article does not focus on those instances.
Handjobs and STD Transmission

Handjobs involve manual stimulation of the penis or clitoris using hands or fingers;. However, considering sexual activity, their risk of contracting STDs remains relatively low due to several reasons:
- Limited Exposure: The outer skin of the penis and clitoris protects against many STDs, which require direct contact with mucous membranes or exchange of bodily fluids to spread. However, since handjobs only involve external genitalia, exposure is drastically decreased.
- No Exchanging of Bodily Fluids: STDs such as HIV, gonorrhea, chlamydia, and syphilis typically spread through a bodily fluid exchange such as semen, vaginal fluids, or blood; handjobs do not involve this activity, therefore further decreasing chances of infection.
- Skin-to-Skin Contact: While STDs like herpes and HPV (human papillomavirus) may be spread through skin-to-skin contact, such as handjobs involving minimal sexual contact risk less likely transmitting infections like these than activities that involve direct sexual communication between partners.
Exceptions and Caveats
While the risk of contracting an STD from handjobs is generally low, there are certain exceptions and essential caveats that must be considered:
- Open Sores or Cuts: Open sores, cuts, or lesions on the genital area increase the risk of transmission as these openings allow viruses or bacteria to infiltrate and multiply.
- Unclean Hands: If the person performing the handjob has recently come into contact with infected genital fluids or any contaminated surface and failed to wash their hands immediately afterward, there is a small risk of transmission.
- Viral Shedding: Certain STDs, like herpes, can be passed from person to person even without showing visible symptoms, which is known as viral shedding and increases risk during sexual contact or even handjobs.
STDs you can get from handjobs

Regarding sexually transmitted diseases (STDs) and handjobs, the risk of transmission is generally lower compared to other sexual activities involving direct genital contact or the exchange of bodily fluids. However, knowing that some STDs can still be transmitted through hand-to-genital or skin-to-skin contact is essential. Here are a few STDs that can be contracted through giving or receiving handjobs:
- Herpes: Herpes can be transmitted through skin-to-skin contact with an infected area, even if no visible sores or symptoms are present. Suppose a person with herpes has active sores on their genitals or surrounding areas. In that case, there is a risk of transmitting the virus through hand-genital contact.
- Human Papillomavirus (HPV): HPV can be spread through skin-to-skin contact, and certain strains of the virus can infect the genital area. While the risk is generally lower with handjobs, it is still possible to transmit HPV if there are any skin cuts, sores, or openings.
- Syphilis: Although syphilis is primarily transmitted through direct contact with syphilis sores (chancres), it is theoretically possible to send the infection through hand-genital contact if there are open sores or lesions on the genital area.
- Molluscum Contagiosum: Molluscum contagiosum is a viral skin infection that can be spread through skin-to-skin contact. If the infection is present on the genitals and there is contact with the infected area, transmission is possible.
It’s important to note that other common bacterial STDs like gonorrhea and chlamydia are primarily transmitted through direct contact with infected bodily fluids (e.g., semen, vaginal fluids). Hence, the risk of transmission through handjobs is generally low. However, if infected fluids are present on the hands and come into contact with the genital area, transmission is still possible.
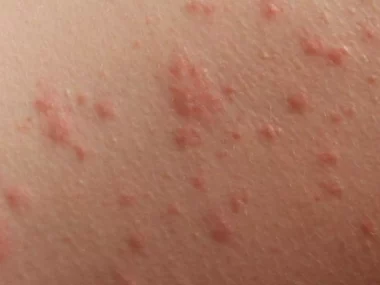
STD/STI Symptoms to look out for

When it comes to sexually transmitted diseases (STDs), the symptoms can vary widely depending on the specific infection. It’s important to note that some STDs may not cause any noticeable symptoms, so regular testing is crucial for early detection and treatment. However, many STDs can produce a range of symptoms that may appear a few days to several weeks after infection. Here are some common symptoms to look out for:
- Unusual Discharge: Unusual discharge from the penis, vagina, or anus is a common symptom of STDs. It may be yellow, green, or white and can have an unpleasant odor.
- Genital Sores or Bumps: Painful sores, ulcers, or bumps may appear on or around the genitals, anus, or mouth. These can be indicative of herpes, syphilis, or genital warts (caused by HPV).
- Pain or Burning Sensation: Pain or a burning sensation during urination or sexual intercourse may be a sign of infections like chlamydia or gonorrhea.
- Itching or Irritation: Persistent itching, redness, or irritation in the genital or anal area could be symptoms of various STDs, including pubic lice or trichomoniasis.
- Abdominal Pain: Some STDs, such as pelvic inflammatory disease (PID) resulting from untreated chlamydia or gonorrhea, can cause abdominal pain or discomfort.
- Flu-like Symptoms: In some cases, people infected with certain STDs, including HIV, may experience flu-like symptoms such as fever, fatigue, sore throat, and swollen lymph nodes.
- Rashes: Some STDs can cause skin rashes on different body parts, like the palms of the hands or soles of the feet. Syphilis, for instance, often produces a characteristic rash.
- Swollen Lymph Nodes: Enlarged or tender lymph nodes in the groin, armpit, or neck can sometimes indicate an infection.
It’s important to remember that these symptoms do not definitively indicate an STD. They can also be caused by other conditions. Conversely, some STDs may not present symptoms, making regular testing and comprehensive sexual health check-ups crucial. Especially if you are sexually active or have multiple partners.
When you notice any of these symptoms or suspect you may have been exposed to an STD. Seeking medical attention and getting tested promptly is essential. Early diagnosis and treatment improve your overall health and help prevent the spread of infections to others. Remember, practicing safe sex and open communication with your sexual partners are essential components of maintaining good sexual health.
Practicing Safe Sex

To reduce the risk of STD transmission during sexual activities, including handjobs, it is essential to practice safe sex. This can involve:
- Communication: Discussing sexual health and STD status with your partner is crucial for informed decision-making.
- Protection: Using condoms or dental dams during sexual activities can provide additional protection against STD transmission.
- Hygiene: Regularly washing hands and genitals before and after sexual activities can help minimize the risk of infection.
- Regular Testing: If you are sexually active or have multiple partners, getting tested regularly for STDs is essential for early detection and treatment.
Can you get an STD from a Handjob? Conclusion
While the risk of getting an STD from giving or receiving a handjob is generally lower than other sexual activities, it is not risk-free. Maintaining good hygiene and protection during sexual activity can further minimize this risk. Suppose there are concerns about STDs or sexual health in general between partners. Open communication must take place to allow both to discuss any concerns openly and honestly before seeking professional medical advice.
Regular testing can ensure long-term sexual well-being as well as overall wellness. If you have any concerns about your sexual health or potential exposure to STDs, seeking advice from a healthcare professional is always recommended.
Remember, being informed and educated about STDs is the first step toward responsible sexual behavior. Let’s dispel myths and spread accurate information for a healthier understanding of sexuality.